Decision Support & Business Intelligence
ALY6060
01
Introduction to Business Intelligence:
Overview of Business Intelligence The Role that BI plays in organizations
Factors that are driving the importance of BI relative to emerging importance of Big Data, Data Driven Decision Making, and maintaining competitive advantage.
Four capabilities of BI:
Organizational Memory, or storage of information that can later be accessed and used.
Information Integration: ability to link structured and unstructured data from a variety of sources,
Business Analytics: ability to create new insights and use them to make better decisions.
Presentation: ability to use appropriate reporting and balanced score cards to make BI more valuable.
Technologies Enabling Business Intelligence
Data warehouses, data lakes, enterprise resources
OLAP
Real-time Decision Support and Analytic Methodologies.
(Data Discovery, Mining, Modeling, Classification, Overview of Machine Learning)
Management and Future of Business Intelligence
BI Data Governance
Organizational Support for BI
Real Case Studies of BI Implementation
02 COMMITTED AND IMMERSED
Preview
- Stakeholder commitment
- Considerations about budget
- Analytical function and its immersion into the business and organization
- Winning strategies that one can apply in the circumstance
- How to become and maintain as member of the decision making group
- How to become a trusted analyst
Stakeholder Commitment
buy-in
noun
noun: buy-in; plural noun: buy-ins; noun: buyin; plural noun: buyins; noun: management buy-in; plural noun: management buy-ins
- a purchase of shares by a broker after a seller has failed to deliver similar shares, the original seller being charged any difference in cost.
- a purchase of shares in a company by managers who are not employed by it.
- the buying back by a company of its own shares.
- agreement to support a decision.
“the CEO got a buy-in from all his vice presidents to launch the new product”
1. Decision as a Process
- Defining decision making
- Defining the decision
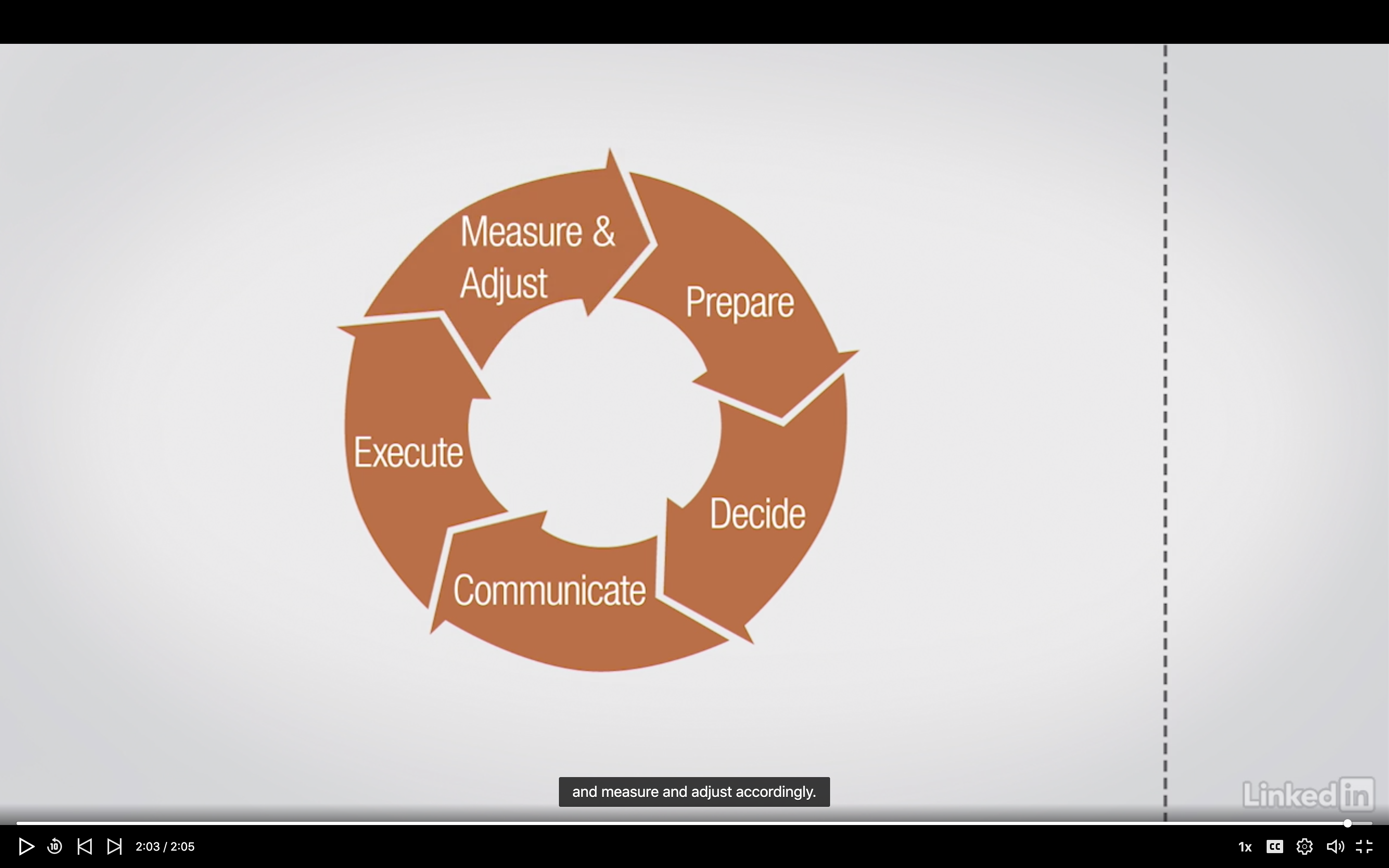
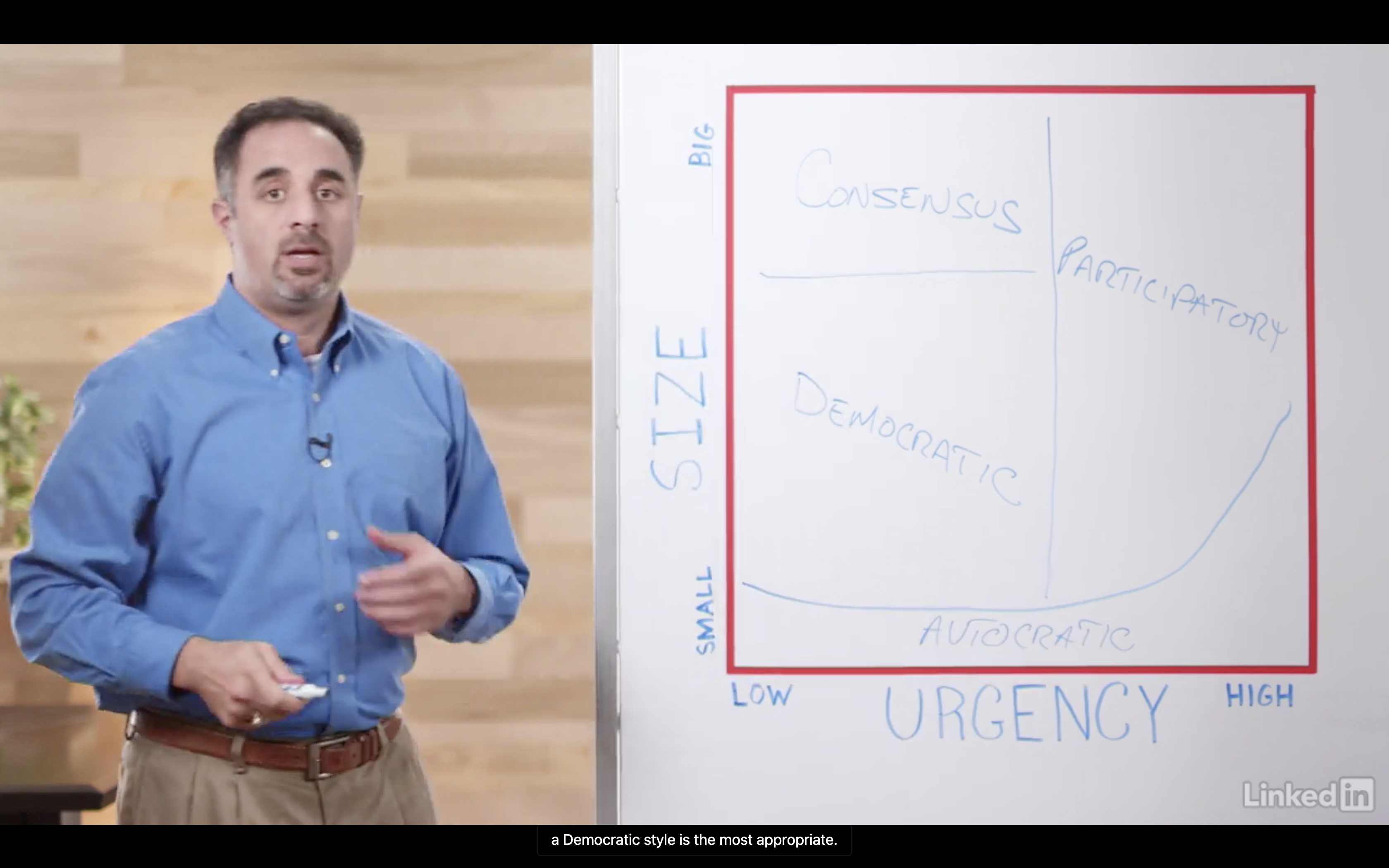
2. The Style of Decision Making
The Style of Decision Making
- Autocratic:
- Participatory
- Democratic
- Consensus-based
Making Autocratic Decision



Making Participatory Decision

Making Democratic Decision
Committee -> Set a deadline -> Vote -> Move on ->

Making Consensus-based Decision

3. Stakeholder management
Involving stakeholders in Decisions
Challenges:
- WHo
- Who do you involve?
- Who is going to be impacted by this decision?
- Whose input do you need?
- Take time
- Let them know the benefits of being involved.
- Clarify roles



__Using RACI Matrix___
Who is involved?
What is their role?
How to communicate out?
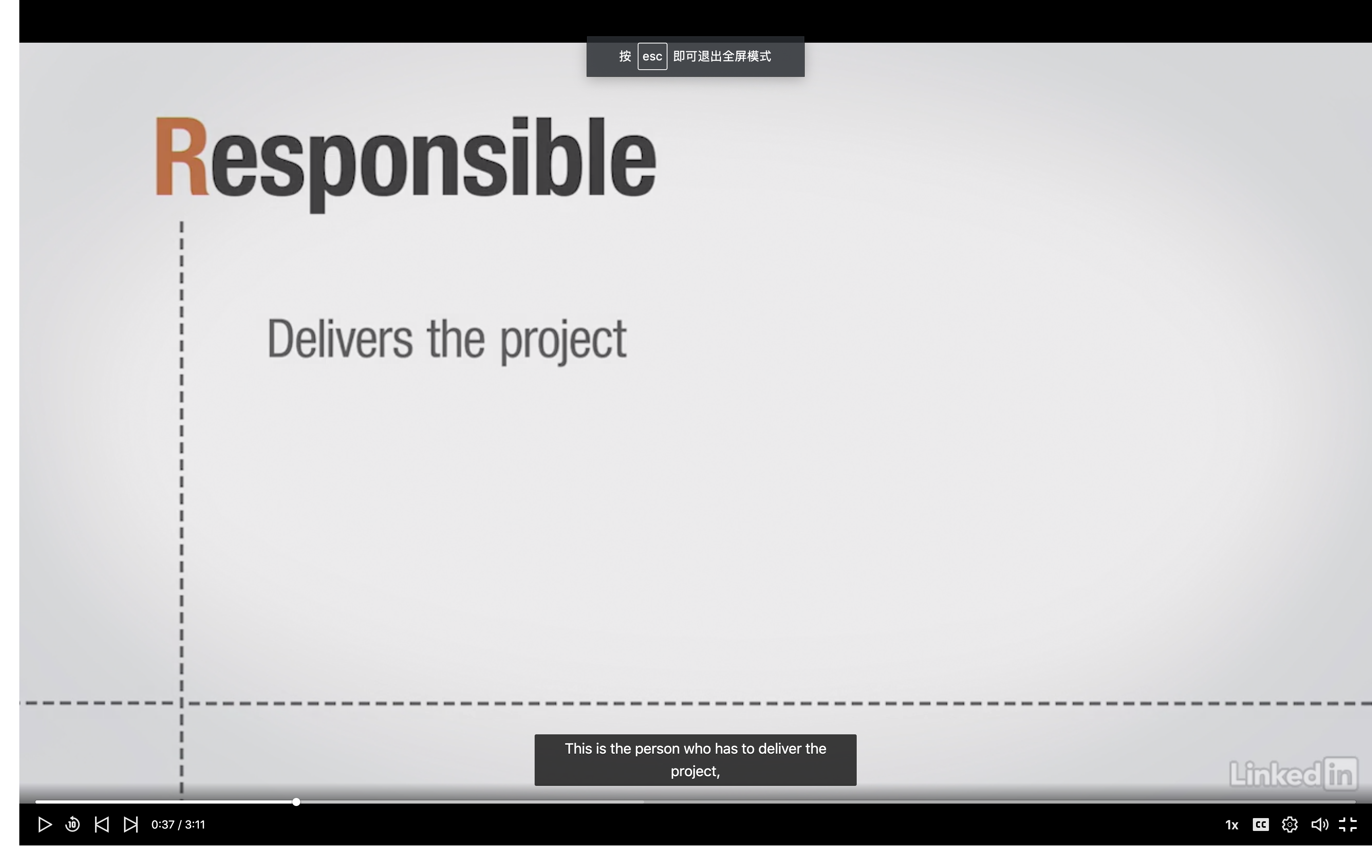



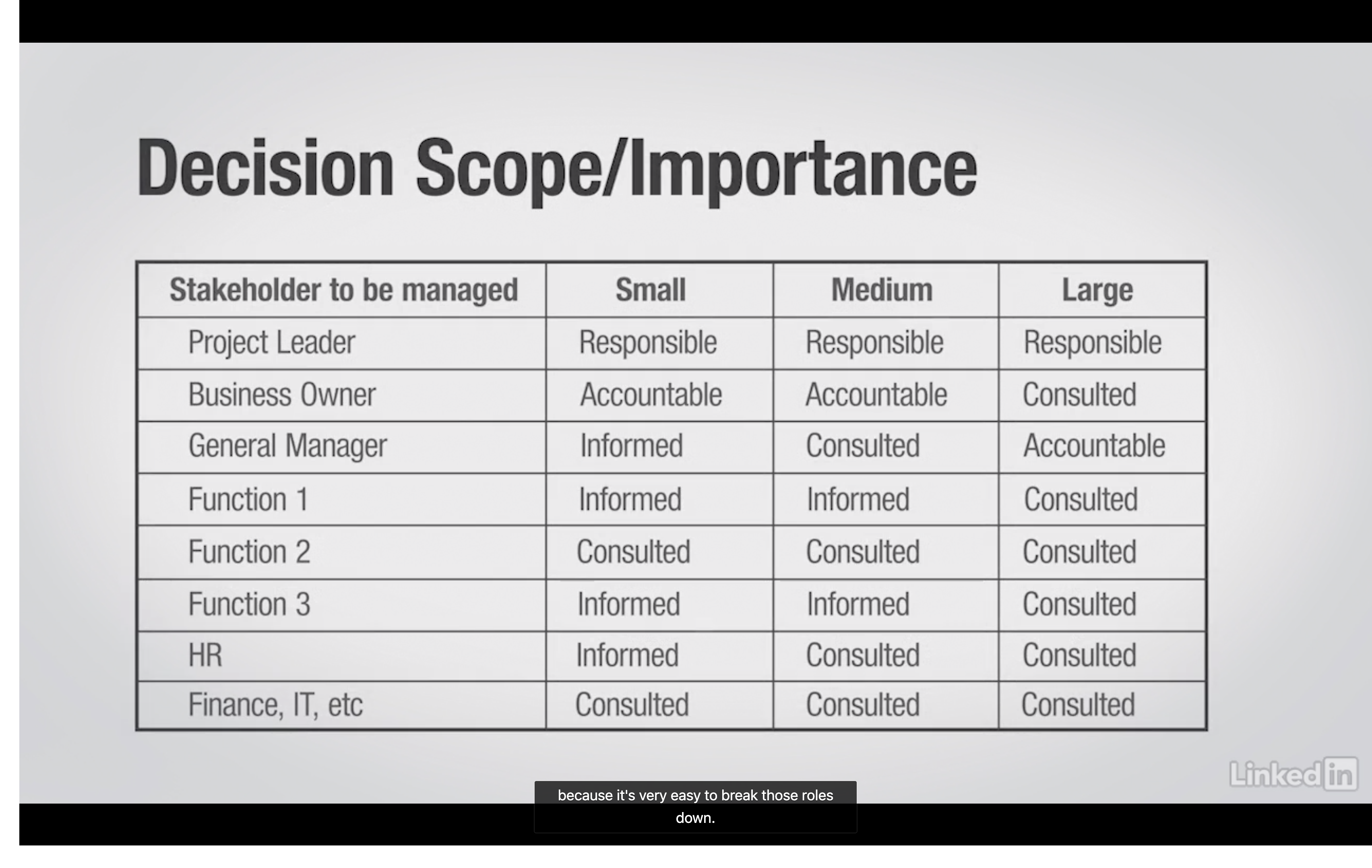
Considerations about budget
One of the most important activities of an analytical function is to develop budgets for the activities that are taking place in a company within the next 12 months. The line items will explain what objectives and decisions are supported by the data, information, and insight that the analytical function is providing.
The objective driven budget is instrumental for resource planning and allocation.
Budget Development Process (I)
In the case of an Analytical or Business Intelligence department, the head of that area will usually ask his team to come up with an analytical planning based on objectives. And then the head would share these information (increase on possible head count and budget) with his business partner to have them decide between each of them.
Budget Development Process (II)
This process usually takes a few weeks or even months of meeting between the analyst and the business partner transparently. A semi-final result of the budget would be decided and then present back to Senior Management by business partner (and analyst if possible). Whom will then review (usually in a Q&A session), and modify objectives or budget.
Budget Development Process (III)
If a change in budget is happening, and in the case of an reduction, business partner together with the analyst should respond to that change, and discuss it with the Senior Management by presenting a budget menu option. Which potentially can result in receiving additional funding.
Budget Development Process (IV)
Change in budgets during the year can be caused by changes in the market conditions, products, customer preferences, etc. It happens all the time and requires agreement between the analyst and the business partner since there’s always a change in expectations along with change in budget. To be able to follow this process, the analyst need to be fully immersed in the business/organization.
Analytical function and its immersion into the business and organization
Let’s start with an example:
Immersed in the Business/Organization
If an analyst does not know about the company’s plan of a product expanded into other market areas, he will not be able to recommend the best possible analytical course of action: e.g. to purchase a specific dataset that will help the company to better understand the market place.
The almost optimal situation – being fully immersed in the business/organization – is achieved, when the analyst was/is part of the decision making process to expand a product into other market areas.
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Anticipation
Immersion lets Analysts to anticipate needs.
In other words, If I know about the plan to expansion by 2019, I can prepare for that in the budget planning process of 2018, and ensure that all the data and report is in place when needed.
Thoroughly immersed in the business means that your business partner recognized your value in decision making and took you in.
Winning strategies that one can apply in the circumstance
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Quick Wins and Predictions
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Quick Wins and Predictions
One way of achieving the seat at the table is to provide Quick Wins~ There are 2 ways to provide value:
• Quick wins when you come new to an organization: e.g. an emerging dataset that let a company better understand switching patterns in drug therapy.
• Establish relationship that analytics develops over the course of months and years: e.g. leading predictive analytics results in excellence in forecast.
What ways to provide value do you see in your organization?
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Winning Strategies
Customer-Centric Growth Winning Strategy
• Find the sweet spots: Excellence in data-driven insight
• Innovate Offer & Experience: Turning insight to action [Data –> Information -> Action]
• Drive customer engagement: Create compelling relationships
Cost Reduction Winning Strategy
• Release the ‘oxygen for growth’: Operational efficiency
How to become and maintain as member of the decision making group
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Value Case for Commercial Business Intelligence
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Value Case for Commercial Business Intelligence
Exemplary benefits for company of USD 8bn revenue
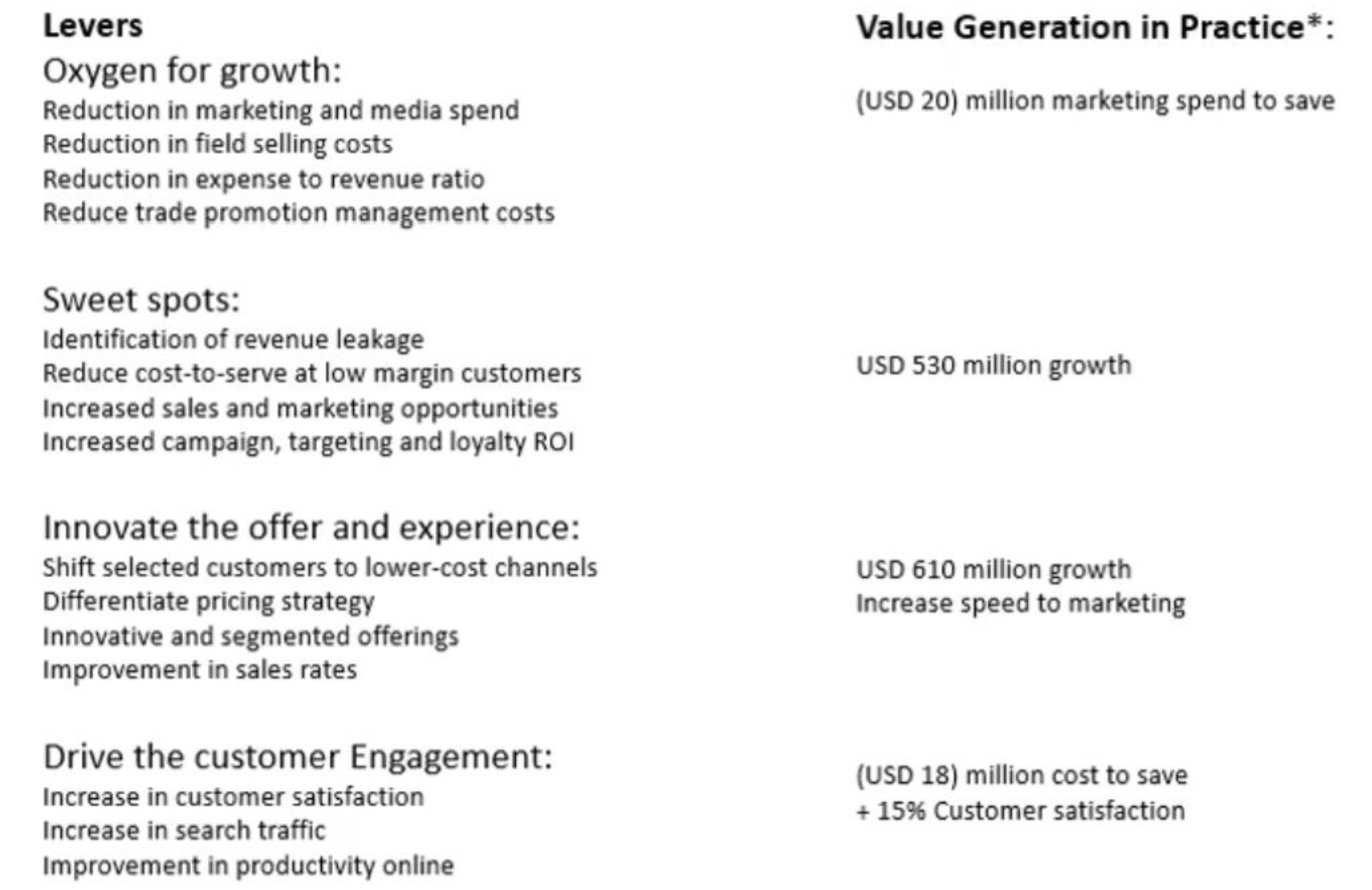
How to become a trusted analyst
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Keep the Seat at the Table
Immersed in the Business/Organization: Keep the Seat at the Table
Being at the table does not mean keep the seat at the table: Analytics need to be a contributor above and beyond the pure analytical function.
• Your ideas and plans should be the one accepted
• You are equipped with creativity, critical thinking, curiosity, and sense of urgency.
Becoming a Trusted Partner
Having a seat at the table
• To educate and advise leadership
Keeping a seat at the table
• Developing keen business acumen
• Developing customer and market insights
• Keeping your Objectivity
• Communicating for impact: Know how and when to assert yourself and your facts
• Exhibiting Emotional Intelligence: resilience, persistence
• Knowing when this is a hill you are willing to die on., And not!
• Getting aligned with a decision you may not agree with
• Striving for Continuous Improvement